RS-485 supports inexpensive local networks and multidrop communications links, using the same differential signaling over twisted pair. It is generally accepted that RS-485 can be used with data rates up to 10 Mbit/s[a] or, at lower speeds, distances up to 1,200 m (4,000 ft). As a rule of thumb, the speed in bit/s multiplied by the length in meters should not exceed 108. Thus a 50-meter cable should not signal faster than 2 Mbit/s.
Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RS-485
Include:
- Module RS-485 (variation for ASTRA controller and ESP32R4 controller)
- RJ-Cable (1m) to: DB9 MALE DTE, DB9 FEMALE DCE, SCREW TERMINAL BLOCK, RJ-12 6P
CONNECT instruction:
ASTRA basic controller:
- Open enclosure. DIP switch setting: all toggle to down (RS MODE).
- Plug in the module to UART2/RS header
- Connect the RJ-cable to port RS (left port)
- Configure firmware: RXD – GPIO16, TXD – GPIO17
ESP32R4 controller:
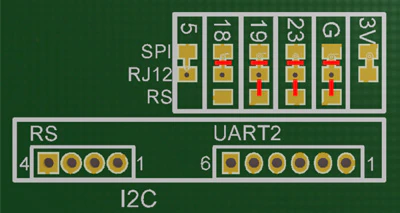
- Configure the soldering jumpers to RS MODE: Cut off jumpers from SPI – G, 18, 19, 23. Solder jumpers RS – G, 19, 23.
- Plug in the module to UART2/RS header
- Connect the RJ-cable to port RS (left port)
- Configure firmware: RXD – GPIO16, TXD – GPIO17
PINOUT:
RJ-12 Pinout (left to fight 1-6):
- – NC
- – NC
- – A+
- – B-
- – GND
- – NC
DB9 pinout:
There are two standard pinout arrangements for the DB-9 connector, DTE and DCE. The Male will be DTE and the Female will be DCE. For a basic RS232 connection, you will only need A+, B-. The Male connector has pins and the Female connector has sockets. The pins are numbered oppositely when looking directly at the connectors.
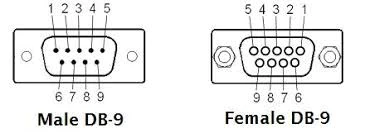

DTE Male DB9
2 – B-
3 – A+
5 – GND
DCE Female DB9
2 – A+
3 – B-
5 – GND
TERMINAL BLOCK
1 – GND
2 – B-
3 – A+
RJ-12
3 – A+ (green)
4 – B- (red)
5 – GND (black)



